|
Stereoscopic vision technology is applied in a wide range of fields, from
3D movies to medical care. Stereoscopic vision makes it possible to observe
images in parallax between both eyes. However, parallax images cannot be
used all the time due to a situation called "occlusion", in which
an object is hidden in the depths by another object. In this case,different
images are projected on the right and left retina. Here, we propose a psychology
experiment to elucidate the function of parvocellular cells in the LGN
of the visual cortex of the brain using occlusion perception.
As a new psychology experiment to clarify whether parvocellular cells in
the LGN of the visual cortex, said to process chromatic and luminance information,
can detect a disagreement between the retinal images produced by each eye,
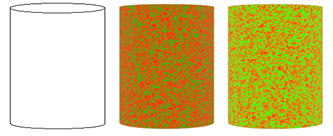
we measured convergence eye movement when gazing at the rim of a column
under occlusion using an equiluminance random dot pattern.
When eye movement prevented the disagreement of the retinal images caused
by occlusion, we thought that convergence eye movement to move both eyes
in front of the rim or divergence eye movement to move them behind the
rim would occur. In other words, we thought that we could clarify whether
there was parvocellular system process agreement or disagreement between
the right and left retinal images under equiluminance. Therefore, we examined
whether a system to detect disagreement between the retinal images exists
in the brain when gazing at the rim of a column onto which an equiluminance
random dot texture was mapped.
Results suggested that the mechanism to avoid disagreement between the
retinal images of the eyes caused by occlusion occurs in the parvocellular
cells, which mainly process color information, as well as in the magnocellular
cells, which process binocular disparity.
Reference
[1]Study on incongruence between binocular images when gazing at the rim
of a column with equiluminance random dots,Shinya MOCHIDUKI, Reina WATANABE,Miyuki
SUGANUMA, Hiroaki KUDO, Noboru OHNISHI,Mitsuho YAMADA,IEICE TRANS. FUNDAMENTALS E101-A(6) 884-891 2018
[2]Eye movement measurement of gazing at the rim of a column in stereo
images with yellow-blue equiluminance random dots、Vol.E102-A,No.9、pp.1196-1204、IEICE
Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer
Sciences,2019,Shinya Mochiduki, Ayaka Nunomura, Hiroaki Kudo
[3]Occlusion Avoidance Behavior During Gazing at a Rim Drawn by Blue-Yellow
Opposite Colors, pp.897-901, 2021,6, Miho SHINOHARA, Yukina TAMURA, Shinya
MOCHIDUKI, Hiroaki KUDO DOI: https://dx.doi.org/ 10.1587/transfun.2020IML0001
 |