
 |
The standard viewing distance for TV images is the distance at which the
scan line structure cannot be seen, based on a person's eyesight. This
was six times the height of the screen (denoted here as gHh) in the NTSC
system TV (525 scanning lines), and 3H for current HDTV images (1125 scanning
lines). Viewing angles at each position were 12 and 30, respectively.
However, advances in high-resolution pictures and practical use of 4K (4000
scanning lines) and 8K (8000 scanning lines) displays are increasing. Such
displays are planned for use at the 2020 Tokyo Olympic Games. The standard
viewing distance for 4K is 1.5H, and that for 8K is 0.75H; meanwhile, the
viewing angles from the viewer extend 60 and 100, respectively.We hypothesized
that viewing distances and viewing locations would influence subjectsf
gaze point distribution when viewing a super-high-definition image at a
short distance.
@Therefore, we measure gaze movement while viewing 4K images when changing
viewing distance and viewing position. In this study, viewing distance
set 3 condition 0.75H (51cm: H is the display height) ,1.5H (102cm) and,
3H (204cm) and viewing position set 3 condition (Left: where 1/4 of the
display width was moved left from the display center; Center: at the display
center; and Right: where 1/4 of the display width was moved right from
the display center). We measure gaze movement while viewing 3 images from
eye movement and head movement, and analyze gazing points.
As a result, the distributions of gazing points were gathered in the screen
center. Signicant difference was shown among the picture, viewing distance,
or viewing position with both the 0.75H and 1.5H conditionscompared with
3H condition.
References, Hideaki Takahira, Shinya Mochiduki, Mitsuho Yamada Analysis of gaze movement
when changing viewing distance and viewing position,IEICE Trans. Infromation
and Systems, Vol.J99-D,No.3,pp.-,Mar. 2016 in Japanese
Shinya MOCHIDUKI, Reina WATANABE,Hideaki TAKAHIRA, Mitsuho YAMADA, Analysis
of head movement during gaze movement with varied viewing distances and
positions, IEICE TRANS. FUNDAMENTALS E101-A(6) 892-899 2018
4K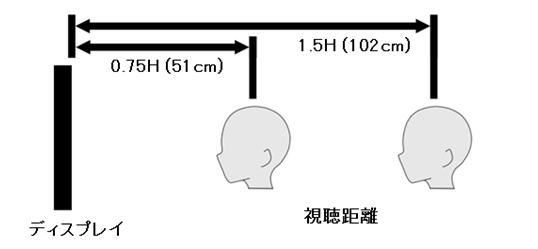
|
 |
|